Metallic bonding examples play a crucial role in understanding the properties of metals and their widespread applications in various industries. From the durability of steel in construction to the conductivity of copper in electronics, metallic bonds are the unseen forces that hold metals together. This type of chemical bonding is unique because it involves a "sea of electrons" that flow freely between metal atoms, giving metals their characteristic properties such as malleability, ductility, and electrical conductivity. In this guide, we will explore metallic bonding examples in detail, shedding light on how this bond works and why it is so essential in both nature and technology.
Metallic bonding is not just a theoretical concept; it has real-world implications that affect our daily lives. Whether you are marveling at the shine of gold jewelry or relying on aluminum foil to wrap your food, you are witnessing the effects of metallic bonds. Understanding these bonds helps scientists and engineers design better materials for everything from aerospace engineering to consumer electronics. By examining metallic bonding examples, we can appreciate the intricate balance of forces that make metals so versatile and indispensable.
For students, educators, and curious minds, exploring metallic bonding examples offers a deeper understanding of chemistry and material science. This article will guide you through the key concepts of metallic bonding, provide practical examples, and answer common questions about this fascinating topic. Whether you're studying for an exam or simply expanding your knowledge, this guide will serve as a valuable resource to help you grasp the complexities of metallic bonding examples.
Read also:Exploring The Life And Legacy Of Johnny Cashs First Wife
Table of Contents
- What is Metallic Bonding?
- Why Are Metallic Bonding Examples Important?
- What Are the Key Properties of Metals?
- Common Metallic Bonding Examples in Everyday Life
- How Does Metallic Bonding Differ from Other Bonds?
- Can Metallic Bonding Examples Be Seen in Nature?
- Why Is Metallic Bonding Crucial for Modern Technology?
- What Are the Industrial Applications of Metallic Bonding?
- How Do Scientists Study Metallic Bonding Examples?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Metallic Bonding
What is Metallic Bonding?
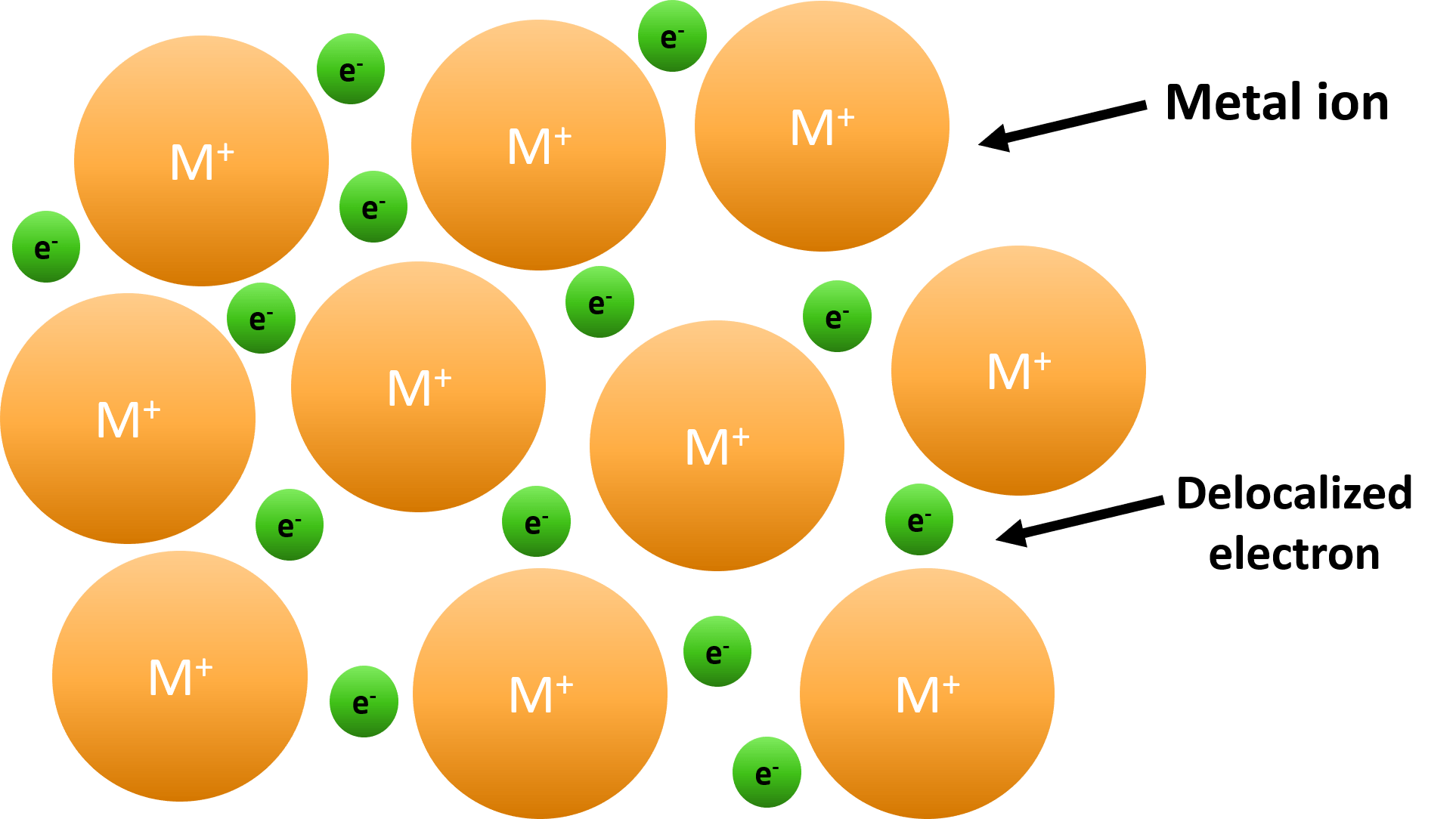
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bond that occurs between metal atoms. Unlike covalent or ionic bonds, metallic bonds involve a "sea of electrons" that are shared among all the atoms in a metal lattice. These delocalized electrons move freely, creating a strong electrostatic attraction between the positively charged metal ions and the negatively charged electrons. This unique arrangement gives metals their distinct properties, such as high melting points, electrical conductivity, and malleability.
Why Are Metallic Bonding Examples Important?
Understanding metallic bonding examples is vital for anyone interested in chemistry, material science, or engineering. These examples help explain why metals behave the way they do and how they can be manipulated for specific purposes. For instance, the conductivity of copper and the strength of steel are direct results of metallic bonding. By studying these examples, scientists can develop new alloys and materials that meet the demands of modern technology.
What Are the Key Properties of Metals?
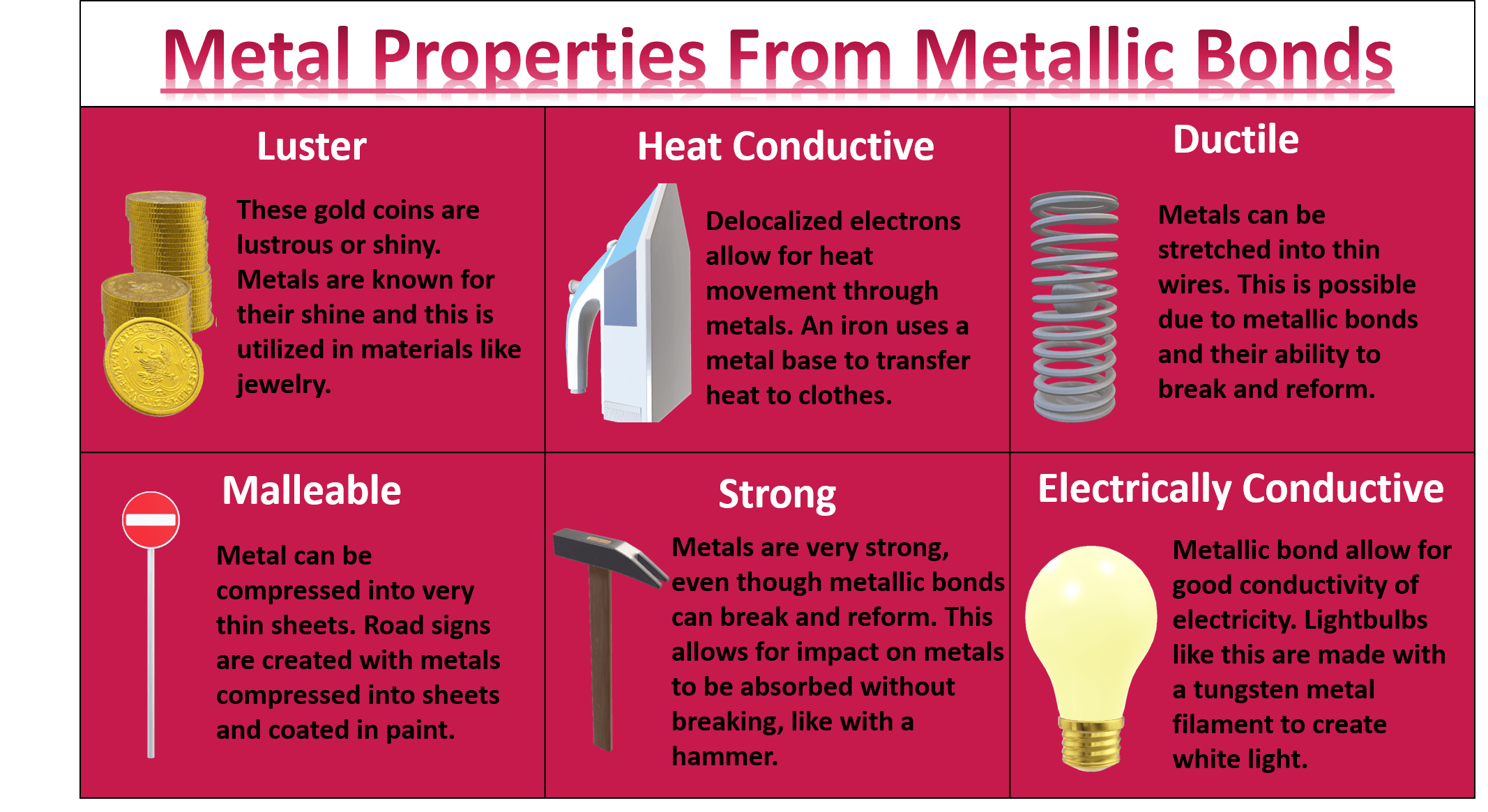
Metallic bonding is responsible for many of the key properties of metals. Here are some of the most notable characteristics:
- High electrical conductivity
- Malleability and ductility
- Shiny appearance (luster)
- High melting and boiling points
- Thermal conductivity
Common Metallic Bonding Examples in Everyday Life
Metallic bonding examples are all around us, often in ways we don't even realize. Here are some of the most common examples:
- Gold Jewelry: The luster and malleability of gold are due to metallic bonding, making it ideal for crafting intricate designs.
- Aluminum Foil: Aluminum's ability to be rolled into thin sheets without breaking is a result of its metallic bonds.
- Copper Wires: Copper's excellent electrical conductivity stems from its metallic bonding, making it a staple in electrical wiring.
- Steel Structures: The strength and durability of steel are attributed to metallic bonding, which is why it's widely used in construction.
How Does Metallic Bonding Differ from Other Bonds?
Metallic bonding is distinct from covalent and ionic bonds in several ways. While covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms and ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, metallic bonding involves a "sea of electrons" that are shared collectively by all atoms in the lattice. This difference explains why metals have unique properties, such as their ability to conduct electricity and their malleability.
Can Metallic Bonding Examples Be Seen in Nature?
Yes, metallic bonding examples are abundant in nature. For instance, the formation of gold nuggets in riverbeds and the presence of iron in meteorites are natural manifestations of metallic bonding. These examples highlight how metallic bonds contribute to the formation of natural materials and their stability over time.
Read also:Discovering Carl Higbie Height Bio And Insights
Why Is Metallic Bonding Crucial for Modern Technology?
Metallic bonding examples are at the heart of many technological advancements. For example, the conductivity of metals like copper and silver is essential for electronic devices, while the strength of titanium alloys is critical for aerospace engineering. Understanding metallic bonding allows scientists to innovate and create materials that meet the demands of modern technology.
What Are the Industrial Applications of Metallic Bonding?
The industrial applications of metallic bonding are vast and varied. Some notable examples include:
- Construction: Steel and aluminum are widely used in building infrastructure.
- Electronics: Copper and gold are essential for wiring and circuitry.
- Transportation: Lightweight metals like aluminum and titanium are used in vehicles and aircraft.
- Jewelry: Precious metals like gold and silver are valued for their luster and durability.
How Do Scientists Study Metallic Bonding Examples?
Scientists use a variety of techniques to study metallic bonding examples, including X-ray diffraction, electron microscopy, and spectroscopy. These methods allow researchers to analyze the structure of metals at the atomic level and understand how metallic bonds contribute to their properties. By studying these examples, scientists can develop new materials with tailored characteristics for specific applications.
Frequently Asked Questions About Metallic Bonding
Here are some common questions about metallic bonding examples:
- What is the role of electrons in metallic bonding? Electrons in metallic bonding form a "sea" that moves freely, creating a strong attraction between metal ions.
- Why are metals good conductors of electricity? The free movement of electrons in metallic bonding allows metals to conduct electricity efficiently.
- How does metallic bonding affect the properties of metals? Metallic bonding gives metals their characteristic properties, such as malleability, ductility, and conductivity.
- What are some real-world metallic bonding examples? Examples include copper wires, aluminum foil, and steel structures.
In conclusion, metallic bonding examples are not just theoretical concepts but practical insights into the materials that shape our world. By understanding these examples, we can appreciate the science behind the metals we use every day and the innovations they enable in technology and industry.