A subgaleal hematoma in adults is a rare but serious medical condition that requires immediate attention. It occurs when blood accumulates between the scalp's galeal layer and the skull's periosteum, often resulting from trauma or injury. While this condition is more commonly associated with newborns during childbirth, adults can also develop it, albeit less frequently. Recognizing the symptoms early can help prevent complications and ensure proper treatment. Understanding what a subgaleal hematoma in adults entails is crucial for both patients and caregivers alike.
Subgaleal hematomas in adults are typically caused by blunt force trauma to the head, such as a fall, car accident, or sports injury. The condition can lead to significant blood loss and swelling, which may increase intracranial pressure. If left untreated, it can result in complications like anemia, infection, or even neurological damage. Therefore, prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to managing the condition effectively.
Despite its rarity, awareness of subgaleal hematoma in adults is growing among medical professionals and the general public. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding what a subgaleal hematoma in adults is, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. By educating yourself on this topic, you can better advocate for your health or the health of a loved one in case of an emergency.
Read also:Damiano David And Dove Cameron Are They Still Together In 2023
- What is a Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults?
- What Causes a Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults?
- Symptoms of a Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults
- How is a Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults Diagnosed?
- Treatment Options for a Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults
- What Are the Complications of a Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults?
- How Can a Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults Be Prevented?
- When to See a Doctor for a Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults
- Conclusion
What is a Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults?
A subgaleal hematoma in adults refers to the collection of blood in the potential space between the scalp's galeal layer and the skull's periosteum. This space is normally tight, but trauma or injury can cause it to expand, allowing blood to accumulate. Unlike other types of hematomas, such as epidural or subdural hematomas, a subgaleal hematoma is located superficially and does not directly affect the brain. However, its size and location can still pose significant risks.
The condition is often mistaken for a simple scalp injury or bruise, especially in its early stages. However, the swelling and discoloration associated with a subgaleal hematoma can worsen over time, leading to complications if not addressed promptly. It is essential to differentiate this condition from other head injuries to ensure appropriate treatment.
What Causes a Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults?
The primary cause of a subgaleal hematoma in adults is trauma to the head. Common causes include:
- Falls, especially in older adults or those with mobility issues
- Car accidents or collisions
- Sports-related injuries, such as those from contact sports
- Assault or physical altercations
In some cases, underlying medical conditions like blood clotting disorders or the use of anticoagulant medications can increase the risk of developing a subgaleal hematoma in adults. Understanding the root cause is critical for both prevention and treatment.
Symptoms of a Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults
Recognizing the symptoms of a subgaleal hematoma in adults is vital for early intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Swelling or a noticeable lump on the scalp
- Bruising or discoloration around the affected area
- Pain or tenderness in the scalp
- Headaches or dizziness
In severe cases, individuals may experience signs of shock due to significant blood loss. If you notice any of these symptoms after a head injury, seek medical attention immediately.
Read also:Bonnie Owens Net Worth A Deep Dive Into The Life And Legacy Of A Country Music Legend
How is a Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults Diagnosed?
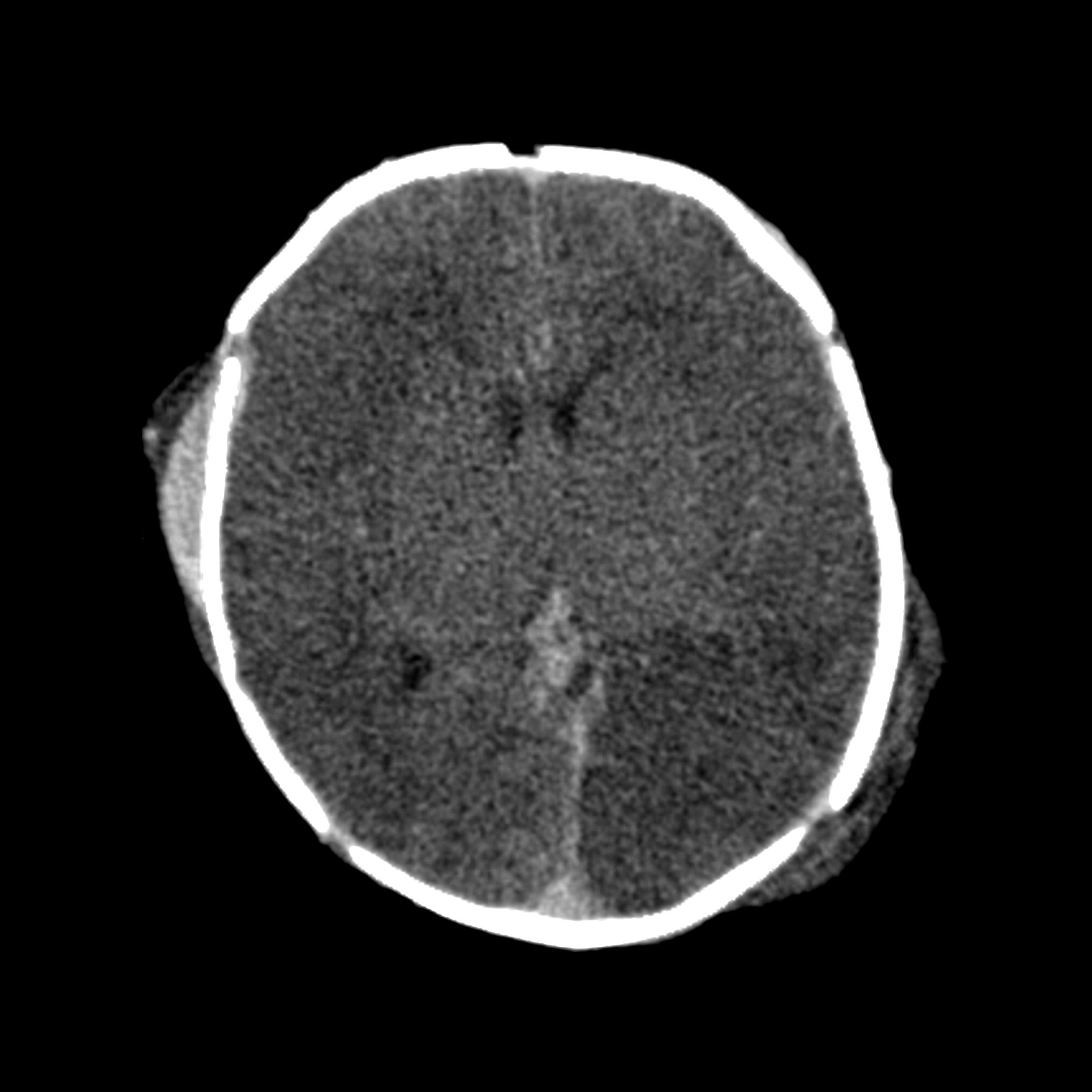
Diagnosing a subgaleal hematoma in adults typically involves a combination of physical examination and imaging tests. A healthcare provider will assess the scalp for swelling, bruising, and tenderness. Imaging tests such as CT scans or MRIs may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions, such as skull fractures or intracranial bleeding.
Treatment Options for a Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults
Treatment for a subgaleal hematoma in adults depends on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, conservative management, such as rest, ice application, and pain relief medications, may suffice. However, more severe cases may require:
- Drainage of the hematoma to reduce swelling and pressure
- Blood transfusions if significant blood loss has occurred
- Surgical intervention in rare cases
What Are the Complications of a Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults?
Complications of a subgaleal hematoma in adults can include:
- Anemia due to blood loss
- Infection at the injury site
- Increased intracranial pressure
These complications highlight the importance of timely diagnosis and treatment.
How Can a Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults Be Prevented?
Preventing a subgaleal hematoma in adults involves minimizing the risk of head injuries. This can be achieved by:
- Wearing helmets during high-risk activities
- Using seat belts while driving
- Ensuring safe environments for elderly individuals
When to See a Doctor for a Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults?
Seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of the following after a head injury:
- Persistent or worsening swelling
- Severe pain or headaches
- Signs of shock, such as rapid heartbeat or dizziness
Frequently Asked Questions About Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults
What is a subgaleal hematoma in adults?
A subgaleal hematoma in adults is a condition where blood accumulates between the scalp's galeal layer and the skull's periosteum, often due to trauma.
Can a subgaleal hematoma in adults heal on its own?
Mild cases may resolve with conservative treatment, but severe cases require medical intervention.
Conclusion
Understanding what a subgaleal hematoma in adults is can make a significant difference in managing this condition effectively. By recognizing the symptoms, seeking timely medical care, and following preventive measures, individuals can reduce the risks associated with this rare but serious condition. Always consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment options tailored to your specific needs.